


Calculation method of strain distribution for forming a flat material into a desired curved surface
Calculation system for determining the shrinkage and elongation allowance required to form a target curved surface from a flat surface
General field of forming curved surfaces from thin materials (metal plates, paper, cloth, fabric, etc.)
Sheet metal, development of original drawings, linear heating, development of three-dimensional toys.
Creation of patterns for fabric products. Design of three-dimensional fabrics.
At shipbuilding sites, the development of original drawings (planking) and linear heating (curved surface forming process) have been carried out according to several rules to form curved surfaces of ship hulls.
On the other hand, the forming process has been left to the skillful hands of skilled workers without knowing where and how much work should be done on the plate.
The purpose of this study is to show where and how much processing should be done among the techniques of skilled workers.
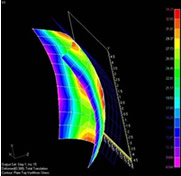
On a flat surface, parallel lines are parallel no matter how far they extend, and the intervals between lines are constant.
On a curved surface, when the spacing between parallel geodesic lines is no longer constant, the surface will wrinkle or stretch when it is extended to a flat surface.
To solve this problem, the target surface is approximated by a function, arbitrary geodesic lines are drawn on the function surface, and the amount of wrinkling and stretching is calculated in advance from the information of the spacing between parallel geodesic lines.
It is expected that the new method will not only make it possible to process without relying on skilled workers, but will also make it possible to form complex shapes that skilled workers have never experienced before.
Furthermore, it will be widely available in the field of forming curved surfaces from flat surfaces.
It is also expected to be applied to the design of patterns for fabric products with complex shapes (clothing, toys, etc.) and the number of stitches in fabrics to match three-dimensional shapes.
・Development of mould expasion and creation of linear heating plans for curved surface forming of thin sheets
・Three-dimensional cutting of fabrics and creation of patterns
・Determination of the number of knits in three-dimensional fabrics, etc.