Practical Examples
Temperature dependences of crystal and nano-structures in
charge-ordering-induced ferroelectric materials

The temperature dependences of crystal and nano-structures in emergent charge-ordering-induced ferroelectric materials were investigated using transmission electron microscopy. We found that the temperature dependences of the crystal and nano-structures of the emergent ferroelectric materials are similar even for different rare-earth ions, although the transition temperatures are different. We also found that the morphologies of the nano-structures differs significantly depending on the size of the rare-earth ions.
Y. Horibe, et al., "Crystallographical and morphological changes in charge-ordering transition of RFe2O4 (R: Y, Lu) investigated by transmission electron microscopy", Ferroelectrics 584, 20 (2021).
Morphological features just below the fracture surface of hydrogen
embrittled stainless steel
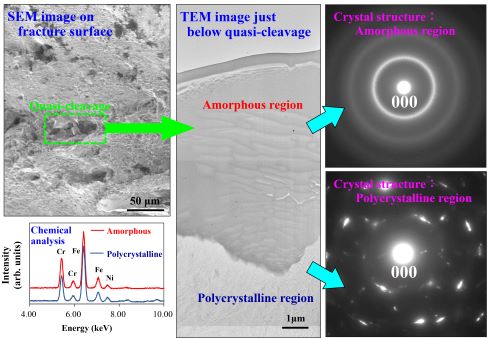
The morphological features just below the fracture surface of hydrogen embrittled stainless steel was studied using transmission electron microscopy. We discovered the appearance of an amorphous region just below the fracture surface, with the chemical composition almost identical to that in the polycrystalline region existing below. In addition, we also found the presence of aggregated regions of voids in the amorphous region.
A. Harada, et al., "Amorphization under fracture surface in hydrogen-charged and low- temperature tensile-tested austenitic stainless steel", Philos. Mag. Lett. 101, 40 (2021).
Nano-structure changes in mixed manganese spinel oxide ZnMnGaO4
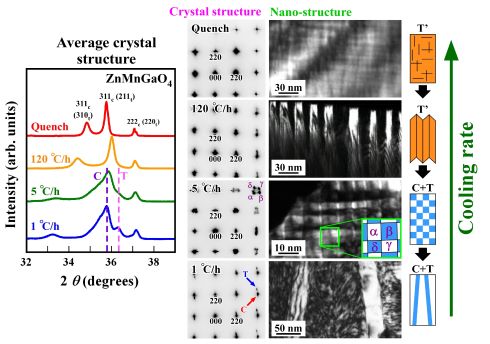
Crystallographic and morphological investigations using transmission electron microscopy were performed in manganese spinel oxides ZnMnGaO4, which is a mixture of manganese spinel ZnMn2O4 and gallium spinel ZnGa2O4. We discovered the existence of nano-structural changes from checkerboard type to lamellar type, depending on cooling rates from high temperatures.
M. Ishimatsu, et al., "Control of nanostructures by cooling rate in spinel-type manganese oxide ZnMnGaO4", Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 59, 105002 (2020).
Nano-structure changes in mixed manganese spinel oxide (Co,Mn,Fe)3O4
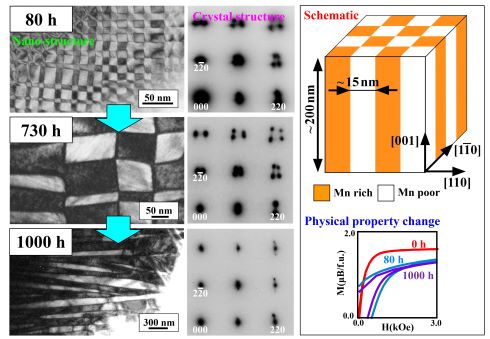
Nano-structure changes in mixed manganese spinel oxide (Co,Mn,Fe)3O4, which is a mixture of the ferrite spinel magnet CoFe2O4 and the manganese spinel CoMn2O4, were investigated using transmission electron microscopy. We discovered that although these materials are ceramics, it is possible to control the nano-structure from the checkerboard type to the lamellar type only by simple heat treatment. We also found a magnetic change due to this nano-structure control.
Y. Horibe, et al., "Self-assembled lamellar-type nanostructure in manganite spinel (Co,Mn,Fe)3O4",
Appl. Phys. Lett. 115, 232401 (2019).
Antiferroelectric crystal structure change in lead-free dielectric material
Bi1-xSmxFeO3

Crystallographic changes due to Sm doping into Bi sites of BiFeO3, which is one of the most famous lead-free ferroelectric material, were studied using transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. We discovered antiferroelectric crystal structure changes with the increase of Sm. We also found that these changes in the crystal structure can be explained by the combinations of characteristic ion displacements.
Y. Horibe, et al., "Quadruple superstructure with antiferroic ionic displacements in Bi1-xSmxFeO3",
Phys. Rev. B100, 024105 (2019).
